Timely detection of deviations in health conditions and risk factors is an opportunity to prevent the development of heart and vascular diseases and extend an active and fulfilling life.
Preventive screening is recommended for all adults - it will help recognize diseases at an early stage and prevent severe cardiovascular catastrophes!
Even in the absence of an established cardiac diagnosis by a physician, it is necessary for individuals with certain predispositions to heart dysfunction to undergo medical examination. These include:
- Frequent stress
- Family history of heart problems
- Excess body weight
- Age older than 45 years.
- Medical Analysis
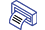
- Electrocardiography (ECG)
Regular ECG testing should be conducted to timely detect diseases. ECG allows identifying initial abnormalities in the heart's function, assessing the dynamics of cardiac pathologies, and evaluating the effectiveness of prescribed therapies.
Although ECG is the most commonly prescribed examination in cardiology, in some cases, it may not provide sufficient information. For an accurate diagnosis, the doctor may recommend other investigations.
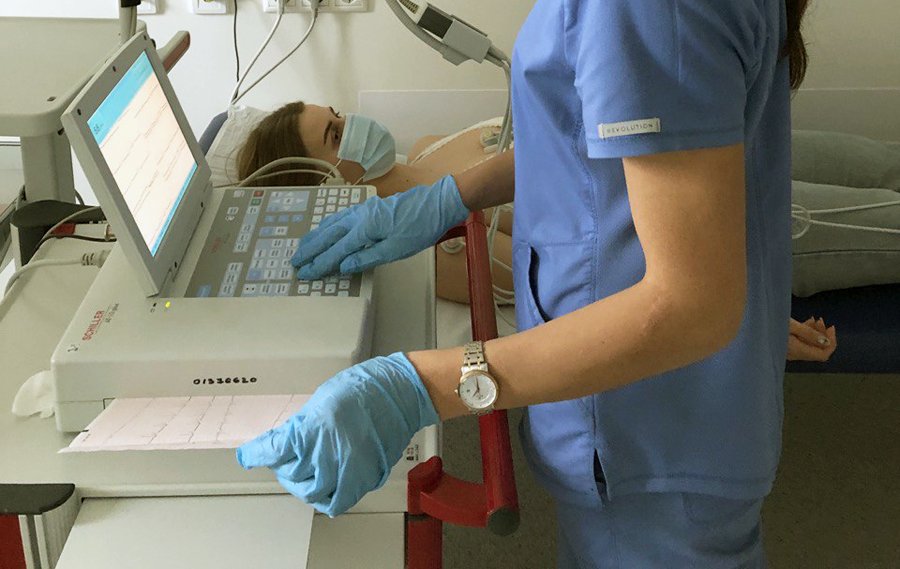
- 24-hour ECG and Blood Pressure Monitoring
This procedure is prescribed to analyze changes in heart activity during sleep, physical activity, meals, smoking, etc.
Depending on the purpose of the study, one of three types of 24-hour monitoring is used:
- Holter monitoring of ECG - an instrumental diagnostic method that involves a 24-hour recording of the patient's electrocardiogram in multiple modified leads using a portable recorder.
- 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring – a diagnostic procedure that involves multiple blood pressure measurements throughout the day and night using a special device.
- Bi-functional monitoring of ECG and blood pressure — a method that includes determining blood pressure during a 24-hour period with simultaneous ECG registration.
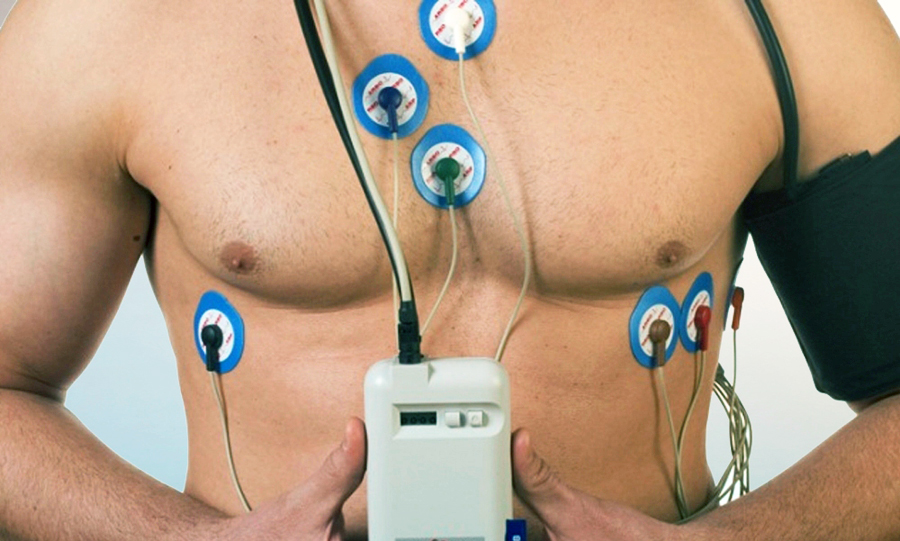
- Cardiac Ultrasound (Echocardiography)
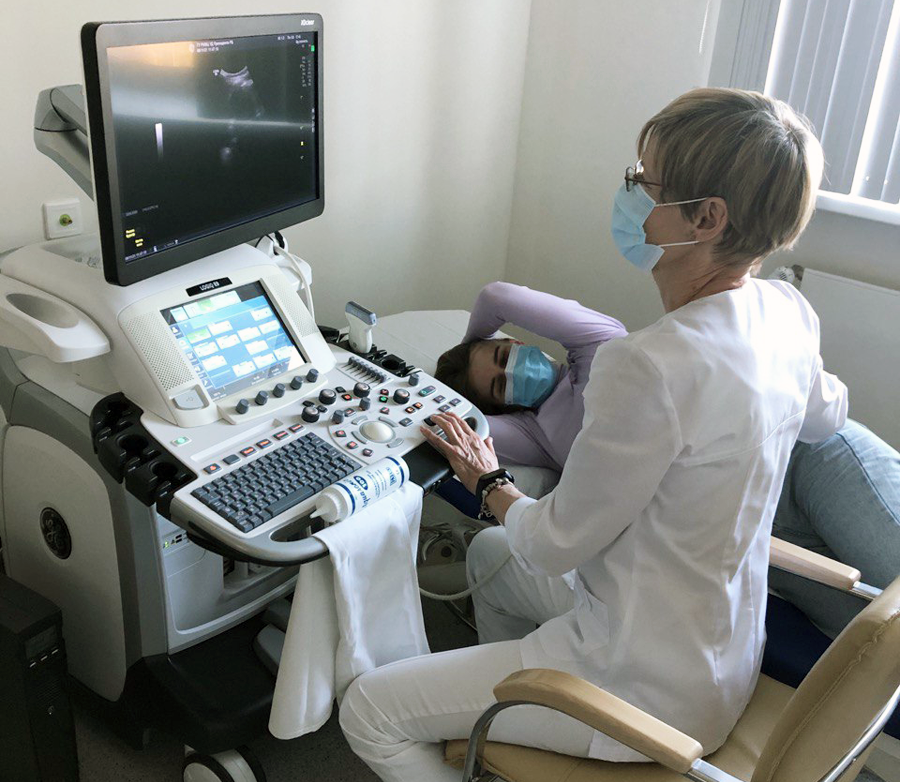
This is a non-invasive ultrasound diagnostic examination of the heart, which allows detecting changes in the heart that may not manifest with any painful sensations and cannot be detected through an electrocardiogram (ECG). At the RCMC, there is a capability to perform the examination in 4-D mode.
- Sleep Disorders Research.

There is a clear link between sleep-disordered breathing and an increased frequency of elevated blood pressure, raising the risk of heart diseases and stroke. Essentially, treating specific forms of sleep-disordered breathing can effectively reduce the chances of developing certain cardiovascular conditions.
Comprehensive analysis at the RCMC allows identifying the risks of developing cardiovascular diseases.
The following laboratory profiles are used for this purpose:
- "CardioRisk" - This profile displays the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases as well as the severity of existing pathologies. It includes complete blood count (CBC), urinalysis (UA), biochemical tests, assessment of the hemostasis system, determination of glycosylated hemoglobin levels, thyroid-stimulating hormone, homocysteine, and specific indicators of heart failure.
- "Stroke Risk" - This profile is used to assess the risk of cerebrovascular disorders and provide a general health assessment. It includes biochemical tests, assessment of the hemostasis system, and an aggregation test.
- "Arterial Hypertension" - This profile is necessary when arterial hypertension occurs at a young or old age, when symptoms suggest secondary arterial hypertension, or when the disease progresses rapidly despite adequate hypotensive therapy. It includes general blood test, biochemical tests, determination of thyroid-stimulating hormone levels, analysis of the aldosterone/renin ratio to evaluate the functional activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, assessment of the hemostasis system, determination of glycosylated hemoglobin levels, and specific indicators of heart failure.
It is worth noting that in the aforementioned profiles, besides several factors helping to detect heart abnormalities, a modern marker of heart failure is investigated - NT-proBNP, the precursor of brain natriuretic peptide.
The BNP level is elevated in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. Moreover, the obtained information about the BNP content in the blood plasma accurately corresponds to the functional classes of chronic heart failure. Determining the BNP level in the blood plasma helps to assess the severity of chronic heart failure, predict the further development of the disease, and evaluate the effectiveness of the conducted therapy.
Monitoring one's health and timely detection of abnormalities are the keys to a long and active life.
Follow the simple rules of a healthy lifestyle: eating right, exercising regularly, not smoking, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption. Try to manage stress and maintain a positive mood.
Do not put off a visit to the doctor, even if you do not experience health problems. Regular preventive examinations will help to identify problems in the early stages and prevent the development of serious diseases.